

Network classes define how many addresses are allowed on the network, with class A being the largest and class C being the smallest. The above table uses Class A, B, and C to define network types. This means that the last 8 bits of the IP address are reserved for host IP addresses, thus IP addresses 192.168.0.15 through 192.168.0.255 will be allowed as host IP addresses on the network. This means that the first 24 bits of the IP address are reserved for network routing.
192.168.0.15 defines the address prefix, and /24 defines the number of bits reserved for the netmask. To understand what CIDR notation means, take the IP address 192.168.0.15 and the /24 CIDR, for example. CIDR accomplishes the same task as traditional subnet masking. It enables network administrators to group blocks of IP addresses into single routing networks.

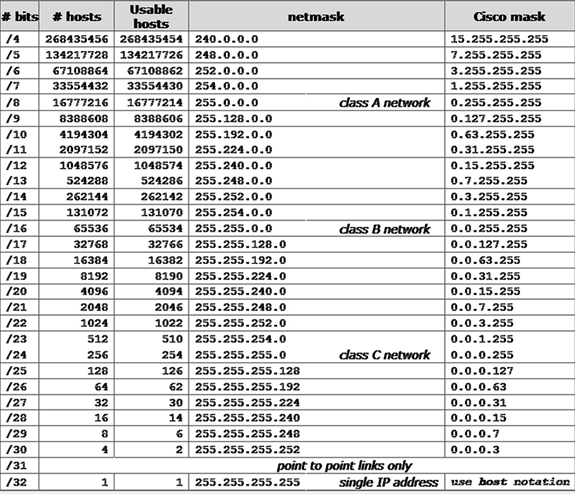
The following table details how many networks and IP addresses are allowed with each CIDR length and equivalent subnet masks.ĬIDR stands for Classlesss Inter-Domain Routing. CIDR defines which IP addresses, and how many host IP addresses will be allowed on the network. Note: The IP address count column shows the total number of IP addresses within each CIDR range, including the network address and broadcast address.CIDR notation accomplishes the same task as network subnet masking.

The following table lists out all the CIDR ranges with the number of IPv4 address within that range: CIDR Range These range from a /0 with the entire IPv4 address space, down to a /32 that only includes a single IP address in the range. Some times it can be difficult to remember how many IP addresses are in each of the CIDR ranges that can be defined. If this sounds a little difficult for you to calculate, then the following calculator and reference table for IPv4 CIDR notations should prove useful. For example, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (in dotted decimal notation) has 24 leading 1 bits, so its CIDR prefix is /24. To calculate the CIDR prefix for a given IP address range, you need to count the number of leading 1 bits in the binary representation of the subnet mask. For example, the CIDR prefix of /24 indicates that the first 24 bits of the IP address represent the network address, while the remaining 8 bits represents the host address. The number represents the number of network bits in the subnet mask, and is used to determine the range of IP addresses that belong to the network. The CIDR prefix is written as a slash followed by a number between 0 (zero) and 32. The network portion and the host portion of an IP address are not fixed, but can be specified by a number known as the CIDR prefix. CIDR notation is commonly used by network engineers, administrators, and Site Reliability Engineers (SRE) to manage IP addresses and create subnets.ĬIDR notation is a flexible and efficient allocation of IP addresses by allowing the use of variable-length subnet masks. IPv4 CIDR notation, specifically, is a way of representing a range of IP addresses in a concise and standardized format. What is CIDR IPv4 Address Range Notation?ĬIDR stands for “Classless Inter-Domain Routing”, and is the method used for assigning IP addresses and routing Internet traffic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
